Chondrodermatitis: An In-Depth Exploration of Causes and Treatments
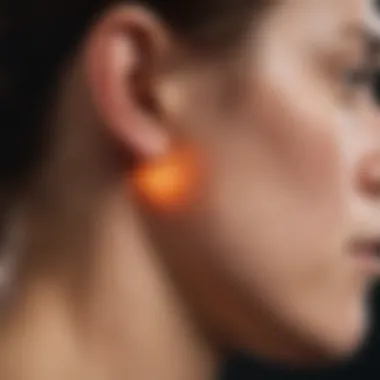

Intro
Chondrodermatitis is a condition that manifests as a localized inflammation of the cartilage and skin, with the auricle being the primary site of affliction. This article seeks to dissect the complexities surrounding chondrodermatitis, providing insightful information on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the broader implications for patients.
Understanding this condition is vital for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike, as it underlines the intersection of dermatological health and cartilage involvement. The impact on quality of life due to pain and discomfort cannot be underestimated, making it essential to explore the nuances of this ailment.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Definition of Key Terms
Chondrodermatitis can be defined as an inflammation affecting both cartilage and overlying skin, leading to painful lesions. The condition may be categorized in various ways, including:
- Chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis – This is the most common form, often appearing as a painful nodule on the auricle.
- Chondrodermatitis inversa – A less prevalent type that can occur.
Concepts Explored in the Article
This exploration will delve into several critical areas:
- Causes – Genetic predisposition, trauma, and environmental factors.
- Symptoms – Notable indicators and their implications for patients.
- Diagnosis – Methods used by healthcare providers to identify the condition.
- Treatment Options – Various approaches to manage symptoms and resolve inflammation.
- Potential Complications – Understanding risks associated with untreated chronic cases.
- Latest Research Findings – Insights from clinical studies and anecdotal evidence.
Findings and Discussion
Main Findings
Research indicates that chondrodermatitis primarily affects older adults, with a higher prevalence in individuals frequently exposed to pressure on the auricle. Effective management strategies are based on the severity and persistence of symptoms. Early intervention can prevent complications, reinforcing the need for awareness about this condition.
Potential Areas for Future Research
Future studies could explore the following areas:
- The efficacy of different treatment modalities, including both medical and surgical interventions.
- Long-term outcomes for patients with chronic chondrodermatitis.
- The impact of lifestyle changes on symptom management and recurrence rates.
Advancements in understanding chondrodermatitis can enhance patient care by tailoring treatment approaches to individual needs.
Understanding Chondrodermatitis
Chondrodermatitis, though commonly overlooked, represents a significant condition that impacts many individuals. Grasping the nuances of this ailment lays the groundwork for better management and treatment. The importance of understanding chondrodermatitis cannot be understated. It allows healthcare providers to accurately diagnose the issue, educate patients, and develop tailored treatment plans. As we progress in our exploration, we will consider how recognition of its symptoms and mechanics is essential for effective intervention.
Definition and Overview
Chondrodermatitis is defined as a localized inflammation affecting both the cartilage and skin, typically observed in the auricle, or external ear. This condition usually presents as painful, tender lesions that may cause both physical discomfort and cosmetic concerns. It primarily arises due to mechanical stress, often exacerbated by sleeping positions or prolonged pressure on the ear. Increased awareness of this condition can enhance patient outcomes, as it enables early diagnosis and evidence-based treatment strategies. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms behind chondrodermatitis is crucial for clinicians and researchers alike, as it can aid in developing preventive measures and more effective treatments.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
The epidemiology of chondrodermatitis indicates that while it can occur in various populations, it predominantly affects older adults, particularly those with a history of skin and connective tissue disorders. The condition is more frequent in men than in women, and incidence rises with age. Additionally, factors such as sun exposure and skin type may contribute to its prevalence. Environmental influences, alongside lifestyle choices, play a role in the susceptibility to chondrodermatitis. Understanding these demographic aspects can inform targeted prevention and treatment initiatives, potentially improving health outcomes for high-risk groups.
"A clear grasp of the epidemiological factors can significantly enhance the management strategies for chondrodermatitis."
The burden of this condition may be underestimated, but recognizing its prevalence is essential for advancing both research and clinical practices related to dermatological health.
Types of Chondrodermatitis
Understanding the different types of chondrodermatitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Each variant presents distinct characteristics and may require specific management approaches. In this section, we will explore three primary types: Chondrodermatitis Nodularis Helicis, Chondrodermatitis Chronica Tributaria, and other variants. This knowledge helps clinicians tailor their strategies and improves patient outcomes by addressing the unique aspects of each type.
Chondrodermatitis Nodularis Helicis
Chondrodermatitis Nodularis Helicis is a common form that typically affects the ear's auricle. Patients often notice a painful, tender nodule that can develop from prolonged pressure, such as sleeping on one’s side. This variant usually emerges in older adults, particularly in males.
The nodules are generally dome-shaped and can have a central crater, which may ooze or crust over. Management often involves conservative measures, including pressure relief and topical treatments. In more persistent cases, injections of corticosteroids can alleviate inflammation. Surgical intervention may be considered if the nodules significantly impair quality of life or do not respond to other therapies.
Chondrodermatitis Chronica Tributaria
This variant, frequently seen in older individuals, is also associated with chronic pressure on the affected areas, including the outer ear. It manifests as a painful, eroded area, typically with accompanying crusting. The lesions are often bilateral and arise where the cartilage experiences friction or irritation, such as during sleep.
Similar to Chondrodermatitis Nodularis Helicis, conservative treatment is the first line of action. Suggested interventions include eliminating sources of pressure, applying topical corticosteroids, and attending to any underlying skin conditions. However, cases may require more aggressive treatments if they do not improve.
Other Variants


Chondrodermatitis can also present in other, less common forms, reflecting a diverse clinical picture. These variants may include atypical presentations in different locations or in conjunction with systemic conditions that affect the skin's integrity and healing.
Some patients may experience localized inflammation that does not fit neatly into the previous categories, requiring an individualized approach. Comprehensive evaluation and collaboration with dermatologists may be necessary for optimal management. It is essential to keep abreast of any new findings or emerging patterns, ensuring that all patient presentations are considered.
Etiology and Risk Factors
The etiology of chondrodermatitis is complex, involving various mechanical, environmental, and systemic factors. Understanding these elements is critical for both diagnosis and treatment. Identifying risk factors allows clinicians to provide more targeted management strategies. Furthermore, knowledge of these factors can also help in educating patients, ultimately contributing to better outcomes and enhanced quality of life for those affected.
Mechanical Factors
Mechanical factors often play a significant role in the development of chondrodermatitis. Pressure on the cartilage and skin is a primary concern. This can stem from various sources, including sleeping positions or prolonged use of headphones. The constant friction can lead to localized inflammation.
- High-risk activities: Certain occupations or hobbies that involve pressure on the ear may increase the likelihood of this condition.
- Age considerations: Older adults may be more susceptible due to factors such as skin thinning and decreased subcutaneous tissue, resulting in less cushioning against pressure.
Clinicians should carefully evaluate the patient's history, taking note of any specific mechanical stressors that could contribute to their symptoms.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors also contribute to the onset of chondrodermatitis. Changes in temperature and humidity can affect skin integrity. Exposure to harsh weather conditions, such as cold or excessive sunlight, can exacerbate symptoms. Dry skin often leads to cracking, creating a gateway for inflammation.
- Climate: People living in extreme climates may face heightened risk, as their skin undergoes more stress.
- Skin care products: The use of irritating substances could play a role, as some individuals may have sensitivities to certain ingredients found in cosmetics or personal care items.
- Allergens: Common allergens in the surrounding environment may aggravate existing skin conditions, contributing to the inflammatory process.
Systemic Conditions
Lastly, systemic conditions can influence the risk and severity of chondrodermatitis. For instance, disorders that compromise the immune system can predispose individuals to skin infections and inflammation. Conditions such as diabetes may impact wound healing, complicating the management of any underlying skin issues.
- Diabetes: Higher blood sugar levels can affect skin health and healing.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions that cause an overactive immune response may make the skin more vulnerable to inflammation and irritation.
- Circulatory disorders: Poor blood circulation affects healing and may also lead to a heightened risk of skin complications.
Understanding these systemic factors is vital for creating individualized treatment plans and monitoring patient progress effectively.
Clinical Presentation
Understanding the clinical presentation of chondrodermatitis is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals. This section delves into the key symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and differential diagnosis associated with this localized inflammation of cartilage and skin. Insight into these elements can significantly aid in timely recognition and management of the condition, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Common Symptoms
Chondrodermatitis generally manifests with specific symptoms that are critical in diagnosing the condition. The most prevalent symptoms include:
- Localized pain: Patients often describe a persistent ache or sharp pain in the affected area, which can worsen with pressure.
- Tenderness: The inflamed site is usually sensitive to touch, making regular activities uncomfortable.
- Skin changes: There may be redness and swelling around the auricle, with possible crusting or scaling of the skin as the inflammation progresses.
- Nodular lesions: In cases like chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis, nodules form on the helix of the ear.
These symptoms not only highlight the condition’s physical manifestations but also point to the need for differential diagnosis to rule out other potential causes of auricular pain.
Diagnostic Criteria
To diagnose chondrodermatitis accurately, healthcare providers typically follow certain criteria. These may include:
- A thorough medical history: Understanding the patient's previous health issues and any related risk factors is key.
- A detailed physical examination: Noting the specifics of the lesions, pain level, and tenderness is fundamental.
A well-conducted patient evaluation can distinguish chondrodermatitis from other similar skin conditions, ensuring correct treatment.
- Diagnostic imaging: While rarely necessary, imaging techniques can rule out other pathologies if symptoms are atypical.
- Histopathological examination: A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and understand the nature of inflammation better.
These criteria guide clinicians toward a more precise diagnosis while forming the basis for developing an effective management plan for patients.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a crucial step in the clinical presentation of chondrodermatitis, as many conditions can exhibit overlapping symptoms. Some common conditions to consider include:
- Basal cell carcinoma: Malignant growths can often mimic chondrodermatitis.
- Psoriasis: Skin plaques can appear similar to the lesions of chondrodermatitis, leading to confusion.
- Eczema: The inflammatory characteristics may overlap, but there are usually distinctive features in eczema that help in its identification.
- Auricular gout: This can also present with localized pain; however, additional clinical signs usually help to differentiate.
Recognizing these conditions through differential diagnosis is critical in tailoring effective treatment strategies. A focused approach to the clinical presentation can guide further assessment and intervention, ultimately benefiting those affected by chondrodermatitis.
Diagnosis of Chondrodermatitis
The diagnosis of chondrodermatitis is essential for both effective management and optimal patient outcomes. Accurate diagnosis allows for differentiation from other similar conditions, ensuring the right treatment is applied. Understanding how chondrodermatitis presents clinically and through diagnostic techniques minimizes misunderstanding and accelerates patient care.
Clinical Examination
A clinical examination is often the first step in diagnosing chondrodermatitis. The healthcare professional typically begins with a thorough history-taking, focusing on the patient's symptoms. Patients may report local pain, tenderness, and discomfort in the affected area, which mainly involves the ear. The physical examination includes observing the ear's structures, looking for specific signs like nodules or ulcerations.


- Inspect the auricle for redness or swelling.
- Palpate the area for tenderness.
- Assess any changes in skin texture or color.
The examination should also consider the duration and frequency of symptoms, any history of trauma, and pre-existing health conditions.
Imaging Techniques
Once a clinical diagnosis is suspected, imaging techniques may be employed to further evaluate the condition. While imaging is not always necessary for chondrodermatitis, it can be useful if there is suspicion of deeper issues or if the presentation is atypical. Common imaging modalities include ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Ultrasound: This can provide real-time images of the cartilage and surrounding tissues, helping to assess any changes or inflammation.
- MRI: Offers detailed views of soft tissue structures, making it easier to evaluate the severity of inflammation or any secondary complications.
Utilizing these imaging techniques can aid in ruling out other otologic conditions, thereby confirming a chondrodermatitis diagnosis.
Histopathological Examination
In some cases, a histopathological examination may be conducted. This involves obtaining a biopsy of the affected area to analyze the tissue under a microscope. A histological assessment can identify specific characteristics of the cartilage and surrounding tissues affected by inflammation as well as confirming chondrodermatitis.
The key steps include:
- Performing a biopsy of the lesion.
- Staining the tissue samples to visualize the cellular structure.
- Assessing for unique histopathological features of chondrodermatitis.
This examination is beneficial for differentiating chondrodermatitis from other dermatological issues, such as basal cell carcinoma or psoriasis, which may display similar symptoms.
Diagnosis of chondrodermatitis often requires a combination of clinical history, physical examination, and imaging; histopathological analysis may further refine the diagnosis to ensure precise treatment.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment approaches for chondrodermatitis are crucial for managing the condition and alleviating patient discomfort. Each strategy must be personalized, as factors such as the type and severity of the disease, individual patient needs, and overall health play significant roles in determining the most effective course of action. This section will cover conservative management, interventional treatments, and surgical options, giving a broader context to the treatment landscape.
Conservative Management
Conservative management is often the first line of approach in treating chondrodermatitis. The goal here is to reduce inflammation and pain without invasive procedures. Common methods include:
- Avoidance of Triggering Activities: Patients are advised to avoid pressure on the affected area. This may involve changes in sleeping positions or the use of protective padding.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory creams or corticosteroids can be beneficial in reducing inflammation and improving symptoms.
- Cold Therapy: Ice packs applied to the area may help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Conservative management often leads to favorable outcomes, especially in early-stage cases. It is non-invasive and carries fewer risks compared to more invasive techniques. However, ongoing evaluation is necessary to ensure the effectiveness of these methods.
Interventional Treatments
When conservative management proves inadequate, interventional treatments may be considered. These options can provide more immediate relief and include:
- Injection Therapy: Corticosteroid injections may be utilized to deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly into the area. This method can quickly reduce inflammation and pain for many patients.
- Physical Therapy: In some cases, physical therapy could be helpful for improving the range of motion and alleviating discomfort associated with chondrodermatitis.
These interventional treatments have shown promise in treating moderate to severe cases that do not respond adequately to conservative measures. They can significantly enhance a patient's quality of life and enable return to daily activities, although possible side effects must be always considered.
Surgical Options
Surgical intervention is typically reserved for more persistent cases that fail to respond to conservative and interventional treatments. Surgical options may include:
- Excisional Surgery: This involves removing the affected tissue. It can be effective in resolving symptoms and preventing recurrence.
- Cryotherapy: This technique uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue. It is a minimally invasive strategy and may be appropriate for certain types of chondrodermatitis.
While surgery often provides significant relief, it can come with risks such as infection or scarring. Therefore, this option should be weighed carefully against its potential benefits.
Surgery is most often a last resort, suitable for those who have not found relief through other means.
Complications and Prognosis
The section on Complications and Prognosis is essential in understanding chondrodermatitis, as it sheds light not just on the immediate effects of the condition but also its long-term implications. Proper insight into potential complications can aid healthcare professionals in adjusting treatment plans and guiding patients through their experiences.
A comprehensive understanding of prognosis helps set realistic expectations for recovery and aids in the management of the condition. Knowing the possible complications also encourages early recognition and intervention, potentially reducing the severity of the disease.
Potential Complications
Complications of chondrodermatitis can arise, impacting both physical healing and psychological well-being. These complications may include:
- Chronic Pain: Extended inflammation can lead to ongoing discomfort, affecting daily activities and quality of life.
- Secondary Infections: Open lesions can make the affected area susceptible to bacterial infections, necessitating additional treatment.
- Hypertrophic Scarring: Damage from inflammation or healing processes can result in raised scars, which may cause further aesthetic concerns for the patient.
- Reduced Activity: Continuous discomfort can inhibit mobility, particularly affecting individuals with active lifestyles.
- Psychosocial Effects: The visibility of lesions and persistent pain can contribute to issues such as anxiety and social withdrawal.
"Awareness and education about potential complications can fundamentally change the management strategy for individuals with chondrodermatitis."
This highlights the necessity for effective communication between healthcare providers and patients regarding possible outcomes and preventive strategies.


Long-Term Prognosis
When evaluating the long-term prognosis for individuals with chondrodermatitis, multiple factors come into play. These factors include the patient’s overall health, adherence to recommended treatment options, and the condition's response to intervention.
In many cases, chondrodermatitis can improve with appropriate management or spontaneously resolve over time. However, chronic cases may lead to:
- Recurrences: Many patients experience flare-ups several times a year, which can further complicate treatment decisions.
- Persistent Changes: Skin texture and appearance may remain altered even after inflammation subsides, leaving some for cosmetic concerns.
- Quality of Life Impact: Ongoing symptoms may lead to chronic frustration and emotional. Importantly, timely and effective management can significantly enhance long-term outcomes.
Current Research and Developments
The scope of current research and developments in chondrodermatitis reflects a growing understanding of the condition and its implications for both patient care and treatment efficacy. By engaging with the latest findings, healthcare professionals are better equipped to identify, manage, and educate patients about chondrodermatitis. The importance of staying abreast of these developments cannot be overstated. As research unveils new insights, practitioners can refine their approaches to treatment and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Recent Studies
Recent studies have substantially contributed to the knowledge base surrounding chondrodermatitis. For instance, investigations have focused on the underlying mechanisms that drive the inflammation process within the auricle, enhancing our understanding of why this occurs in some individuals and not others. Studies utilizing advanced imaging techniques have uncovered greater details about the cartilage health in patients.
Furthermore, there has been a notable increase in the exploration of conservative treatments and their effectiveness versus interventional methods. A study published in a dermatological journal highlighted that transitioning from invasive interventions to non-invasive treatments, like cryotherapy or steroid injections, often leads to improved patient satisfaction.
Some key findings include:
- Chondrodermatitis appears more frequently in individuals with certain mechanical predispositions, such as frequent pressure from headphones or prolonged exposure to cold.
- Awareness of the psychological impact of chronic conditions like chondrodermatitis has led to a more comprehensive care model, acknowledging the mental well-being of patients.
- Highlighting the role of genetic predispositions can help in identifying at-risk populations earlier, allowing preemptive measures.
"Continued research and a multidisciplinary approach can significantly enhance the management of chondrodermatitis, leading to better patient-centric solutions."
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in managing and understanding chondrodermatitis integrate both medical and technological advancements. There is a notable shift towards personalized treatment plans based on individual risk factors and response to previous treatments.
Some emerging trends are:
- Telemedicine consultations are becoming more common, allowing patients to engage with specialists remotely. This improves access to care and enables timely interventions.
- Collaboration between dermatologists, rheumatologists, and pain specialists is increasing, reflecting the complexity of chondrodermatitis and the need for holistic treatment strategies.
- Research into newer pharmacological agents shows promise, particularly in areas such as biologics, which target specific pathways involved in inflammation.
- Awareness campaigns and educational resources are evolving, aiming to inform both healthcare providers and patients about the importance of early detection and management of chondrodermatitis.
Overall, the commitment to refining our approaches to treating chondrodermatitis will ensure that patient care is not only effective but also aligned with the latest scientific advancements.
Patient Perspectives
Understanding patient perspectives on chondrodermatitis is essential for a comprehensive exploration of this condition. This segment highlights the subjective experiences of individuals affected by chondrodermatitis. It sheds light on how the condition influences their daily lives, mental health, and overall well-being. By considering patient experiences, healthcare providers can better tailor treatment plans and support systems. Moreover, prioritizing patient feedback can help in the development of effective medical strategies.
While clinical studies provide crucial data, the real-world implications of chondrodermatitis can often differ. Patients frequently describe feelings of frustration and discomfort due to the physical symptoms and the visibility of the condition. These personal narratives are pivotal in grasping the true impact of this inflammation beyond mere clinical definitions.
Patient Experiences
Each person's journey with chondrodermatitis is unique. Many patients report initial signs of discomfort that often progress to visible lesions, which can be distressing. For some, pain management becomes a central concern as the condition can interfere with daily activities. Common feelings shared by many patients include embarrassment and anxiety over their appearance and health.
For instance, one patient noted, "I was self-conscious about the bumps on my ear. They made me feel like others were looking at me differently." Another individual expressed, "The pain was not just physical; it affected my social life. I avoided meeting friends because I didn’t want them to see my ear."
Such experiences illustrate the profound psychological effects chondrodermatitis can impose on individuals. The emotional toll can be significant, necessitating a holistic approach to treatment that addresses both physical and emotional health.
Support and Resources
Patients with chondrodermatitis can find solace and guidance through various support resources. Numerous organizations focus on dermatological conditions and patient welfare. These programs often offer information on managing symptoms and connecting patients to peer networks.
- Online Forums: Platforms like Reddit provide a space for individuals to share their stories and advice. These communities can be comforting for those feeling isolated in their struggles.
- Local Support Groups: Many cities host support groups that meet regularly. These gatherings foster a sense of camaraderie among patients.
- Educational Resources: Websites like Britannica offer valuable insights into chondrodermatitis and its implications. Educational pamphlets distributed by clinics are also useful.
Accessing these resources can empower patients, giving them tools to cope with their condition and connect with others facing similar challenges. They offer not only information but also a sense of belonging and understanding amid the discomfort of chondrodermatitis.
Future Directions in Research
The path forward in understanding chondrodermatitis involves rigorous exploration and inquiry into underexamined areas. Insights gained from future research will not only improve patient care but also broaden the knowledge base for healthcare professionals. Addressing the complexities of this condition through scientific investigation holds the potential to develop novel interventions and refine existing treatment modalities.
Areas Needing Investigation
Future research should consider several critical aspects of chondrodermatitis that remain inadequately explored:
- Etiological Factors: Understanding how environmental and mechanical factors contribute to the onset of chondrodermatitis requires deeper inquiry. Research into specific triggers in various populations could yield tailored preventive strategies.
- Genetic Predispositions: Investigating genetic factors that may predispose individuals to chondrodermatitis can inform personalized medicine approaches. This information can lead to risk assessments based on family histories.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Most studies focus on short-term treatment results. Research concentrating on the long-term outcomes of treatment, including recurrence rates and quality of life aspects, is essential.
- Patient Perspectives: More qualitative research about patients’ experiences with chondrodermatitis can provide richer insights into the psychosocial impacts of the condition. This can help tailor support systems for affected individuals.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
To truly advance the understanding of chondrodermatitis, a multidisciplinary strategy is vital. Collaboration among dermatologists, rheumatologists, physiotherapists, and patient advocacy groups can enhance research quality. Some potential interdisciplinary approaches include:
- Collaborative Research Initiatives: Forming consortia that unite various specialties can encourage sharing of knowledge and resources, paving the way for comprehensive studies.
- Integrative Therapies: Exploring adjunct therapies such as physiotherapy or occupational therapy in conjunction with conventional treatments may reveal synergistic effects that improve patient outcomes.
- Patient Engagement: Involving patients in research design can lead to studies that reflect real-world challenges faced by those suffering from chondrodermatitis, ultimately making research more relevant and impactful.
"Interdisciplinary collaboration fosters innovation and ensures a more holistic approach to healthcare challenges."
Each of these pathways signifies a step toward a more profound understanding of chondrodermatitis and ultimately promoting better care and quality of life for patients.







