Hyoid Suspension for Effective Sleep Apnea Treatment
Intro
Sleep apnea is a disruptive sleep disorder that affects many individuals, leading to a variety of health issues. One promising approach that has emerged in the landscape of treatment options is hyoid suspension. This surgical technique represents a vital piece of the puzzle in understanding how anatomy and sleep disorders interact. Hyoid suspension aims to improve airway stability by repositioning the hyoid bone, a small U-shaped bone located in the neck that plays a crucial role in maintaining an open airway during sleep.
In the quest for better sleep health, the link between anatomy and functionality is becoming clearer. This article delves into the intricate relationship between the hyoid bone and sleep apnea, offering a comprehensive look at the procedure itself, its implications, and outcomes for various patient demographics.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Understanding sleep apnea is crucial, not just for patients but also for medical practitioners, as it lays the groundwork for exploring various treatments, including innovative surgical options like hyoid suspension. Sleep apnea, characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can have serious implications on health, affecting both physical and mental well-being.
When we talk about sleep apnea, the focus should be on its nature and the quite significant impact it has on those who suffer from it. The condition often goes unnoticed initially, obscured by symptoms that may seem benign. However, its consequences can be quite severe, leading to conditions such as hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and even daytime fatigue that can transform a person's life.
A solid grasp of the types and intricacies of sleep apnea helps in recognizing effective treatment options. For instance, hyoid suspension surgery is a novel approach aimed at improving airway stability by positioning the hyoid bone correctly during sleep.
Professionals armed with knowledge about sleep apnea's mechanisms and types can tailor their treatment approaches, leading to better patient outcomes. Understanding the fundamental aspects of sleep apnea not only aids in diagnosis but serves as a springboard to discussing practical interventions, making this exploration vital in our quest to mitigate the effects of this pervasive disorder.
Defining Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can be defined as a sleep disorder where a person's breathing repeatedly stops and starts. It might sound trivial at first, but it can lead to serious health issues if left unchecked. Patients often experience loud snoring followed by choking or gasping sounds, indicating partial or complete obstruction of the airway. This condition can lead to low oxygen levels in the blood and disrupt the natural sleep cycle, resulting in fragmented sleep.
Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is primarily categorized into three types: obstructive, central, and complex. Each type possesses distinct characteristics, causes, and ways they impact the body. Understanding these differences is fundamental to determining appropriate treatment methods.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most prevalent type of sleep apnea. It occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, blocking the airway. One of the key characteristics of OSA is the recurrent episodes of breathing cessation during sleep, often noticed by sleeping partners. It's a significant focus of this article because its relationship with hyoid suspension surgery offers a novel angle of treatment.
The unique feature of obstructive sleep apnea lies in its direct link to obesity and lifestyle choices, which can exacerbate the condition. While OSA can be effectively managed through continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, not all patients respond favorably to it. Here is where hyoid suspension presents itself as a beneficial alternative, particularly for those who seek surgical interventions.
Central Sleep Apnea
Central sleep apnea (CSA), unlike OSA, is characterized by the brain's failure to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. This condition is less common and is often associated with underlying health problems such as heart failure or stroke. The key distinction that makes CSA particularly interesting is its connection to neurological issues rather than obstructive factors.
Patients with central sleep apnea may find challenges in finding effective treatment since typical interventions for obstructive apnea may not be applicable. Here, innovative approaches like adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV) are often employed, though this article emphasizes the potential of hyoid suspension as a less conventional method to address CSA.
Complex Sleep Apnea
Complex sleep apnea syndrome, often referred to as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, is a hybrid of the previous two types. Patients may initially present with obstructive sleep apnea, but during the course of treatment, they develop central sleep apnea characteristics. What makes this type noteworthy is its dual nature, which complicates management strategies.
It becomes imperative for clinicians to monitor and adjust treatment plans continually when dealing with complex sleep apnea. While CPAP may work for obstructive components, its effectiveness can wane as central characteristics emerge. This interplay of mechanisms can make hyoid suspension an intriguing alternative worth exploring for these patients as well.
Prevalence and Impact
Sleep apnea's prevalence is indeed staggering. Estimates suggest that millions of individuals globally are affected, many of whom remain undiagnosed due to lack of awareness or misinterpretation of symptoms. This condition not only detracts from quality of sleep but also poses a risk for developing severe health complications, making understanding and early detection of utmost importance.
The impact of untreated sleep apnea extends beyond the individual to broader society, leading to increased healthcare costs and lost productivity. As awareness grows, it is essential to consider effective treatment options, such as hyoid suspension, as potentially transformative measures for those struggling with this disorder.
Anatomy of the Hyoid Bone
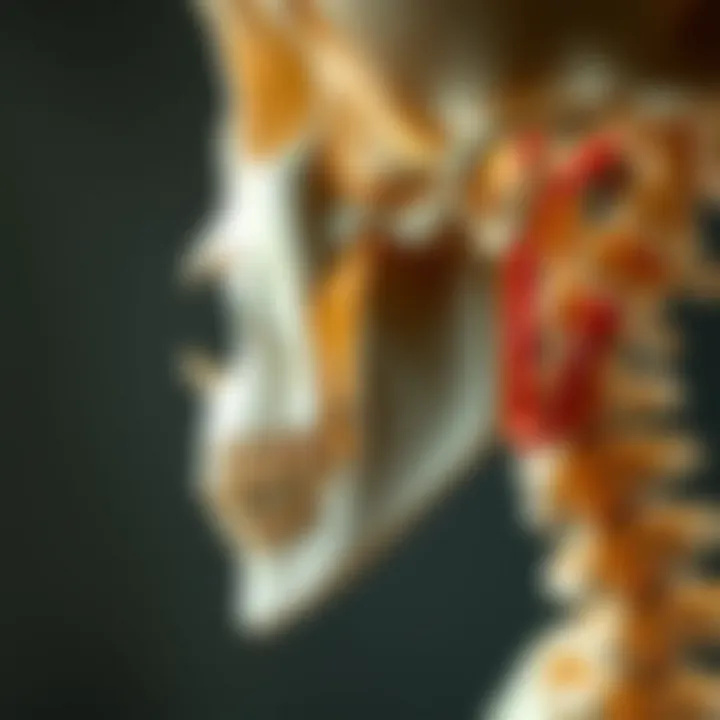
The hyoid bone, often regarded as a unique entity in human anatomy, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the structural integrity of the airway. Nestled in the neck, it has no direct articulations with other bones, making it a floating bone, and this characteristic is central to its function. Understanding the anatomy of the hyoid bone is indispensable for grasping its involvement in sleep apnea treatment. This section elucidates the location, structure, and how these aspects serve its functional significance in airway dynamics during sleep.
Location and Structure
The hyoid bone is located between the mandible and the thyroid cartilage. It is shaped somewhat like a horseshoe, featuring a body, greater horns, and lesser horns. The bone is positioned anteriorly to the cervical vertebrae and serves as an anchor point for several muscles and ligaments. This unique position is crucial as it allows for free movement during swallowing and tongue activities; it acts almost like a scaffold supporting the muscles of the neck and providing stability to the laryngeal structures that play a role in breathing.
- Shape: Horseshoe-shaped
- Components: Body, greater horns, lesser horns
- Location: Beneath the mandible, above the thyroid cartilage
This very architecture ensures that the hyoid supports various essential functions, from phonation to respiration. In particular, hyoid displacement can directly influence the patency of the upper airway, making its anatomy particularly relevant in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea.
Functional Significance
The functional importance of the hyoid bone cannot be overstated. It serves multiple roles crucial to respiratory health. First off, it acts as an attachment site for muscles that control the tongue and the larynx. This is vital, as a well-positioned tongue maintains an unobstructed airway during sleep.
In essence, the hyoid helps in:
- Aiding Swallowing: It provides leverage for the tongue and muscles responsible for swallowing.
- Maintaining Airway Stability: Proper positioning of the hyoid contributes to maintaining airway openness, which is crucial during sleep to prevent obstructions.
- Regulating Phonation: As it supports laryngeal movements, it plays a role in sound production and speech.
The soft tissues surrounding the hyoid, along with the bone's own structural properties, contribute to airway dynamics. If the hyoid is either hypoplastic or improperly positioned, this can exacerbate conditions like sleep apnea.
Relation to Airway Dynamics
The relationship between the hyoid bone and airway dynamics is a complex interplay somewhat akin to a well-choreographed dance, where every move influences the next. In the context of sleep apnea, the position of the hyoid is instrumental in determining the airflow path during sleep. When the hyoid is situated correctly, it helps prevent the collapse of the airway by supporting muscular tone and positioning.
To delve deeper:
- Airway Obstruction Risks: If the hyoid is tilted or retropositioned, muscle tone may decrease, increasing the likelihood of airway collapse and consequent apnea events.
- Interventions: Hyoid suspension surgery aims to reposition this bone to counteract the effects of airway obstruction caused by its dynamic relationship with adjacent structures during sleep.
The position and functionality of the hyoid bone serve not just anatomical purposes but also play a critical role in the treatment and management of sleep apnea. Understanding this aspect provides a foundation for exploring more advanced therapeutic options, such as hyoid suspension surgery, which can directly target the complications arising from its malpositioning.
Hyoid Suspension: A Surgical Overview
Hyoid suspension surgery stands as a crucial intervention in the management of sleep apnea. This procedure is not just a workaround; it addresses the root causes of airway obstruction that many patients face. Understanding its significance can empower both patients and healthcare practitioners to make informed decisions. Instead of relying solely on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines or dental devices, hyoid suspension offers an anatomical solution that can provide long-term relief.
A key feature of hyoid suspension is its ability to enhance stability in the upper airway. By repositioning the hyoid bone, this surgical technique aims to open up the airway, lessen obstructive episodes, and improve breathing patterns during sleep. Moreover, the benefits extend beyond just alleviating symptoms. Many patients report enhanced quality of life post-surgery, resulting in better overall health outcomes.
In considering this procedure, one must weigh the pros and cons. Some advantages of hyoid suspension include its potential for lasting results and decreased daytime sleepiness. However, there are also considerations regarding surgical risks, postoperative recovery time, and the individual’s unique anatomical characteristics.
Indications for Surgery
Before recommending hyoid suspension, healthcare providers evaluate several factors. The most common indications include severe obstructive sleep apnea that has not responded to other forms of treatment. Patients may successfully avoid surgery if they benefit from lifestyle changes, weight loss, or CPAP therapy.
Some factors that may lead to consideration of surgery include:
- Severity of Sleep Apnea: Patients with moderate to severe cases are often ideal candidates.
- Structural Issues: Those with significant anatomical issues like a large neck circumference or a retrognathic mandible may benefit.
- Failure of Conservative Treatments: Patients who do not achieve satisfactory results with CPAP or oral appliances are also suitable candidates.


Surgical Techniques
Procedure Description
Hyoid suspension involves reattaching the hyoid bone to surrounding structures using surgical sutures. The actual process typically takes around one to two hours. Surgeons create small incisions in the neck region to access the hyoid bone, thereby minimizing visible scars. One key characteristic of this procedure is its minimal invasiveness compared to other surgical options, making it a beneficial choice for many patients.
The overall aim is to achieve better airway patency. Surgeons utilize various methods, such as the use of titanium screws for stability, to ensure the success of the procedure. A unique feature of this approach is how it also reinforces the tongue base, which further supports airway opening. The advantages then become clear: enhanced airway size, reduced work of breathing, and a generally smoother sleep experience for the patient.
Postoperative Care
Proper postoperative care is paramount to the success of hyoid suspension. Immediate care often includes pain management, monitoring for any complications, and instruction on activity limitations. Most patients are encouraged to avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks while recovery progresses.
A key characteristic of postoperative care in this context is the gradual resumption of regular activity. Patients typically require follow-up appointments to assess healing and ensure that the airway remains patent. Unique features include the potential need for a follow-up sleep study to evaluate the success of the intervention. While most patients do recover well, some may experience swelling or discomfort. Understanding these potential outcomes can prepare patients for what to expect in their recovery journey.
Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, hyoid suspension carries risks that demand consideration. It includes but is not limited to:
- Infection: As with all surgeries, there is a risk of infection in the surgical wound, affirming the importance of proper wound care.
- Vascular Injury: Given the proximity of critical blood vessels, there’s a chance of vascular injury during the procedure.
- Continued Sleep Apnea: While the intent is to alleviate symptoms, not all patients experience complete success.
Each of these risks requires a comprehensive pre-operative discussion to ensure informed consent and understanding.
Efficacy of Hyoid Suspension in Treating Sleep Apnea
The role of hyoid suspension in the management of sleep apnea cannot be overstated. As a surgical intervention, hyoid suspension aims to stabilize the airway, reducing episodes of obstruction that plague individuals with sleep apnea. Understanding its efficacy involves exploring clinical outcomes, comparative studies with other treatments, and the critical task of identifying the right candidates for this type of procedure.
Clinical Outcomes
Success Rates
Success rates in hyoid suspension surgeries are promising, often reported to range from 60% to 80%. This statistic is crucial because it suggests that a significant number of patients experience improvement in their symptoms post-surgery. The key characteristic that sets these rates apart from other treatment modalities is the direct structural alteration made to the airway. By anchoring the hyoid bone, the surgical technique reduces the collapsibility of the upper airway during sleep.
This improvement is particularly notable as it may lead to decreased reliance on Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices, which many patients find cumbersome or uncomfortable. However, it’s vital to note that while the success rates are appealing, they vary based on factors like the specific surgical technique used, the surgeon's expertise, and individual patient factors like age and severity of their condition. One unique advantage is that hyoid suspension may be more favorable in patients where non-surgical methods have failed, offering a viable alternative when other options appear exhausted.
Long-term Effects
Looking at the long-term effects of hyoid suspension showcases another layer of efficacy. Many studies indicate that patients tend to maintain favorable outcomes over the years. This sustained improvement often includes a decrease in daytime drowsiness, enhanced sleep quality, and lower incidences of airway obstruction episodes during sleep.
A noteworthy aspect of these long-term effects is that they often translate into better overall health, reducing risks associated with untreated sleep apnea, such as cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential drawbacks; some patients might experience discomfort or a perception of altered throat function post-surgery. The importance of follow-up visits cannot be overstated, as they allow healthcare providers to monitor these longer-term outcomes and address any issues promptly.
Comparative Studies
Versus CPAP
When comparing hyoid suspension to CPAP therapy, one considerable advantage emerges: comfort and ease of use. While CPAP machines can be effective at alleviating sleep apnea symptoms, many find the devices intrusive or hard to incorporate into their nightly routine. Hyoid suspension, by contrast, offers a one-time surgical solution that promotes lasting benefits without the need for nightly equipment. However, it's important to consider that CPAP therapy has established itself as a frontline treatment option due to its non-invasive nature and straightforward application.
Patients hesitant about surgery can find reassurance in the consistent results from CPAP studies, emphasizing its continuous validity as a dependable choice for sleep apnea management.
Versus Other Surgical Interventions
Hyoid suspension often stands its ground when placed side by side with other surgical approaches like uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or maxillomandibular advancement (MMA). Hyoid suspension typically involves fewer risks compared to some of these more invasive procedures. A key characteristic of hyoid suspension is its targeted approach to airway obstruction, addressing a specific anatomical issue rather than making broader alterations that may lead to a more complex recovery process.
Moreover, the relatively quick recovery time associated with hyoid suspension can play a significant part in its appeal. However, it’s essential to recognize that patient outcomes can vary based on complex factors and individual anatomy. In some cases, a combined approach with other surgical strategies may yield the best results.
Patient Selection Criteria
Determining the right candidates for hyoid suspension is a crucial aspect of its efficacy. Successful outcomes are often contingent upon a thorough preoperative assessment, which considers factors such as body mass index, severity of obstructive symptoms, and the specific anatomical characteristics of the airway. An individualized approach allows for optimized treatment strategies that significantly enhance the likelihood of success.
Ultimately, the efficacy of hyoid suspension as a treatment for sleep apnea represents a promising avenue for many patients. With ongoing research contributing to improved understanding and techniques, its role in the clinical setting appears to be growing, offering both patients and healthcare providers a valuable tool in the fight against sleep-disordered breathing.
Advancements in Research
The field of sleep medicine is experiencing rapid evolution, especially regarding innovative surgical interventions like hyoid suspension. The importance of advancements in research cannot be overstated, as they directly impact patient outcomes, surgical techniques, and overall understanding of sleep apnea as a multifaceted disorder. Research in this area provides pivotal insights that guide clinicians and researchers in optimizing treatment protocols and elevating patient care.
In recent years, exploring hyoid suspension has gained traction, framing it as a more viable solution among existing options. The knowledge extracted from clinical trials and peer-reviewed studies reveals nuances not only in the effectiveness of the procedure but also in its appropriateness for different patient demographics. This research helps identify which populations might benefit most, thus aligning treatment strategies with individual patient needs.
The importance of understanding the anatomical intricacies and functional significance of the hyoid bone sets the groundwork for these advancements. Further studies highlight correlations between hyoid positioning and severity of airway obstruction, emphasizing the hyoid bone's vital role in maintaining airway stability during sleep. This knowledge is key to improving both surgical outcomes and postoperative care strategies.
Recent Innovations
Recent innovations in hyoid suspension techniques have focused on enhancing precision and clinical effectiveness. Notable recent findings include:
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Some centers have begun employing robotic technology for hyoid suspension procedures. This method enables greater precision, which may lead to reduced recovery times and lower complication rates.
- Fluorescence Imaging: This emerging technique helps visualize airway dynamics during surgery. Utilizing fluorescence, surgeons can assess oxygen saturation in real-time, aiding in optimized positioning of the hyoid bone.
- Customizable Surgical Implants: The advent of tailored implants based on individual anatomies has shown promise. These implants can be designed using 3D printing technology, ensuring a better fit and improved surgical outcomes.
These innovations signify a shift toward more personalized approaches in managing sleep apnea, bridging a significant gap between traditional practices and modern medical technology. Furthermore, ongoing trials regarding their efficacy provide critical data that will shape the future direction of surgical practices in this field.
Future Directions in Treatment
Looking ahead, the future of hyoid suspension and related treatments for sleep apnea appears promising. Some key avenues worth exploring include:
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Strengthening ties between sleep specialists, otolaryngologists, and orthodontists will foster holistic treatment approaches, improving patient referral processes and care continuity.
- Longitudinal Studies on Efficacy: Larger scale and long-term studies are needed to assess the durability of hyoid suspension results over time. By tracking patient outcomes over years, researchers can gather insights about its sustainability compared to non-surgical interventions like CPAP.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Implementing more sophisticated imaging methods pre- and post-surgery may enhance the understanding of airway mechanics. This could aid in preoperative planning and postoperative assessments, ensuring a more tailored approach to treatment.
- Patient Education and Informed Consent: Enhancing knowledge about hyoid suspension among patients can impact treatment acceptance and satisfaction. Creating comprehensive educational materials will empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their care.
Closure
In the intricate landscape of sleep apnea treatment, hyoid suspension surgery emerges as a compelling option that warrants attention. This conclusion synthesizes the key points discussed in this article, focusing on the significance of hyoid positioning and its direct correlation to airway stability. A thorough understanding of the hyoid bone’s anatomy and its functional significance enriches our perspective on how this surgical approach can mitigate the effects of sleep apnea.
Summary of Findings
The efficacy of hyoid suspension has been substantiated through diverse clinical outcomes. Numerous studies highlight a notable improvement in airway dynamics post-surgery, leading to reduced apnea-hypopnea indices in patients.
- Success Rates: Longitudinal studies reveal that about 70-80% of patients experience significant reductions in both the frequency and severity of apnea episodes following hyoid suspension.
- Long-term Effects: Patients generally report enhanced sleep quality, leading to an overall improvement in quality of life. Moreover, follow-up assessments indicate sustained benefits for many, occasionally extending beyond five years post-operation.
These findings bolster the argument for personalized treatment plans that may include hyoid suspension as a viable option.
Implications for Practice
As practitioners navigate the complex management of sleep apnea, the inclusion of hyoid suspension in the surgical toolkit expands therapeutic possibilities. Understanding the nuances of this procedure can significantly alter patient outcomes. Important considerations include:
- Patient Selection: Identifying candidates who exhibit anatomical features that may benefit from hyoid suspension is crucial. This includes patients who have significant tonsillar hypertrophy or other anatomical obstructions.
- Surgical Expertise: Surgeons should focus on training and sustaining skills specific to hyoid suspension to minimize risks and enhance effectiveness. Collaborative approaches with sleep specialists can also improve decision-making.
- Patient Education: Engaging patients in detailed discussions regarding the benefits and potential risks of hyoid suspension empowers them to make informed decisions about their treatment pathways.
Ultimately, hyoid suspension is not just a surgical option; it represents a paradigm shift in how sleep apnea can be approached at a surgical level. By refining the understanding and execution of this procedure, healthcare professionals can position themselves at the forefront of advancing sleep-related interventions. For further reading, resources such as Sleep Medicine Reviews and PubMed can provide valuable insights into ongoing research and clinical practices.







