Comprehensive Guide to Malt Lymphoma Symptoms
Intro
MALT lymphoma, short for Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue lymphoma, is a particular type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma noted for its ties to mucosal tissues in the body. Understanding the symptoms of this disease is essential, not just for well-informed medical practitioners but also for individuals keen to recognize potential signs in themselves or loved ones. The symptoms are diverse, ranging from relatively common indicators to more subtle manifestations that could easily go unnoticed at first.
As we unpack the symptoms, we will highlight key concepts and terminology related to MALT lymphoma. This groundwork serves to equip readers with a foundational understanding, which can also aid in better comprehension of future conversations surrounding this illness. It’s about making the medical language accessible and ensuring clarity on what's being discussed.
MALT lymphoma primarily arises in tissues in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and other mucosal sites, often associated with various chronic inflammatory conditions. Therefore, patients may exhibit symptoms linked not only to the lymphoma itself but also to the underlying conditions.
In this article, we will delve deep into the nuanced presentation of symptoms, explore the risk factors involved, and the crucial role of diagnostic measures. This presentation aims to enlighten both those in the medical field and the general public, fostering a grasp of MALT lymphoma that aids in better management and early detection. The journey begins with a look into key concepts that underpin the understanding of this unusual lymphoma.
Intro to Malt Lymphoma
Malt lymphoma is often overlooked despite being a significant subset of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. By grasping the fundamentals of this condition, we can better appreciate the nuances surrounding its symptoms and overall impact on patient health. This understanding not only benefits healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating patients effectively but also empowers patients and their families to recognize critical signs and seek timely medical intervention.
Definition and Classification
Malt lymphoma, short for mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma, arises from lymphoid tissue associated with mucosal organs such as the stomach, intestines, and lungs. This distinction is important because it helps categorize the lymphoma based on its site of origin. Within Malt lymphoma, one can find various subtypes, reflecting the diverse histological appearances and clinical behaviors. Some prominent classifications include:
- Gastric malt lymphoma: The most commonly encountered form, often linked with chronic gastritis and Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Intestinal malt lymphoma: Less prevalent, but can lead to abdominal pain, bleeding, and other gastrointestinal complications.
- Pulmonary malt lymphoma: Emerging as a significant variant, involving the lungs and potentially leading to respiratory symptoms or complications.
Acknowledging this classification is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment strategies and prognostic outcomes.
Epidemiology
Examining the epidemiology of malt lymphoma sheds light on its incidence, prevalence, and demographic factors associated with the condition. Several key points to consider include:
- Incidence rates: Malt lymphoma accounts for about 5% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas but shows variation based on geographic location. For example, gastric malt lymphoma is more prevalent in regions where Helicobacter pylori infections are common.
- Demographics: The majority of cases are seen in adults, with a slight male predominance. The median age of diagnosis hovers around 60 years, yet cases in younger individuals do occasionally emerge.
- Risk factors: A history of autoimmune diseases, chronic infections like H. pylori, and environmental factors may increase susceptibility to developing malt lymphoma. Understanding these connections is vital for both prevention strategies and patient education.
In summary, recognizing malt lymphoma's fundamental attributes allows for an informed discussion on its symptoms, enhancing awareness and facilitating early intervention. Those engaged in healthcare, education, or research can benefit from a thorough grasp of this condition, ultimately contributing to better outcomes for affected individuals.
Understanding the Symptoms
Malt lymphoma can present an intricate array of manifestations that are crucial for early identification and effective management. Understanding these symptoms is pivotal for both patients and healthcare providers. Recognizing the signs early can substantially affect treatment outcomes and overall patient care. Not only does grasping the nuances of these symptoms empower patients, but it also informs clinicians in making swift diagnostic decisions, which is vital in a landscape where time is often of the essence in managing malignancies. Moreover, given that malt lymphoma is associated with mucosal tissues, the symptoms may not be immediately recognizable, making awareness all the more important.
Common Symptoms of Malt Lymphoma
Common symptoms of malt lymphoma include a range of presentations that can vary widely among individuals. A few notable symptoms include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: This can be a red flag. Sudden or significant weight loss without dietary changes or increased physical activity can indicate an underlying issue.
- Night Sweats: These are not mere discomforts. Profuse sweating during sleep that leaves the bedding drenched can be an alarming symptom pointing toward lymphoma.
- Fever: Persistent low-grade fevers can often be overlooked. If someone finds themselves feeling feverish repeatedly without a clear infection, it may warrant further investigation.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness that doesn’t improve post rest could suggest that the body is under stress from an illness.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the neck or armpits, can often be the first noticeable sign.
These symptoms, while common, can also overlap with other health conditions. Thus, distinguishing malt lymphoma from other ailments necessitates a keen observation of the onset, duration, and accompanying effects of these symptoms.
Localized vs Systemic Symptoms
Understanding the difference between localized and systemic symptoms can shed light on the variation in malt lymphoma presentations.
- Localized Symptoms refer to manifestations that occur in specific areas of the body. For instance, if malt lymphoma primarily affects the stomach, patients might experience discomfort, pain, or a feeling of fullness after eating small meals. This localized impact is significant as it often relates to how advanced the lymphoma is in specific sites.
- Systemic Symptoms, on the other hand, have a broader impact on overall health. These can affect multiple systems, an example being the fever and night sweats mentioned earlier. Systemic symptoms indicate that the body is responding to a widespread condition, which may signal a more advanced stage of the disease. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for placements of interventions.
Chronic Symptoms: An Overview


Chronic symptoms associated with malt lymphoma can sometimes masquerade as more innocuous issues, making early detection challenging.
- Prolonged Bloating: This may present as a frequent feeling of fullness, often mistaken for dietary causes or gastritis.
- Recurrent Infections: If someone is experiencing frequent or unusual infections, it can be attributed to an impaired immune response, which might result from the lymphoma’s interference with normal body functions.
- Persistent Abdominal Pain: Pain that does not subside can be indicative of gastrointestinal involvement. It's essential to address these issues before they compound into more serious health threats.
Chronic symptoms like these can lead an individual down a path of misunderstanding their health status. The distinction between what’s normal and what requires intervention can be blurry, but vigilance is key.
Identifying chronic symptoms early is vital. Those plagued with persistent issues should seek comprehensive evaluations—even if they dismiss these feelings as typical stress or fatigue. Healthcare providers must maintain a high index of suspicion when assessing patients with such unexplained symptoms, guiding them toward timely diagnostics and care.
Symptoms by Location
Understanding symptoms by location in malt lymphoma is critical as it helps to pinpoint the areas affected by this disease. Each specific location can reveal unique symptoms, which in turn can guide diagnostic and treatment pathways. Being aware of how malt lymphoma manifests in different regions of the body allows for a more tailored approach to patient care, improving outcomes significantly.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to quicker interventions, making it essential for both patients and healthcare providers to familiarize themselves with these manifestations.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Gastrointestinal symptoms are quite commonly associated with malt lymphoma, especially since this type of lymphoma often arises in the gastrointestinal tract. Patients may experience a variety of troubling signs that can range from mild discomfort to severe complications.
Common gastrointestinal symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bloating and gas
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
It’s crucial to understand that these symptoms can sometimes mimic other gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome or infections. However, if a patient experiences persistent or worsening symptoms, it’s vital to consult a healthcare provider for further investigation. Signs like unexplained weight loss or significant changes in bowel habits warrant immediate attention. Being aware of these details can help healthcare professionals make better-informed decisions during evaluations.
Ocular Symptoms
Ocular symptoms, while less prevalent than gastrointestinal ones, can occur in malt lymphoma and might manifest as the tumors develop near the ocular region or when lymphatic fluid builds up due to the disease. Symptoms can include:
- Blurred or decreased vision
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Swelling around the eyes
- Dryness or excessive tearing
Patients might dismiss such symptoms as ordinary eye strain; however, a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist could reveal underlying issues related to malt lymphoma. Awareness of ocular symptoms is important because they can indicate the disease is either advancing or affecting critical areas of the body, which necessitates prompt attention.
Pulmonary Symptoms
Pulmonary symptoms in malt lymphoma are not as commonly discussed but can occur, especially if lymphatic tissues in the lungs are affected. Symptoms to look out for include:
- Coughing, which may be chronic or persistent
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Chest pain or tightness
- Recurrent respiratory infections
Recognizing these symptoms is important as they could easily be attributed to other respiratory issues, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). If a person with a history of malt lymphoma begins to notice these respiratory changes, it is essential to seek medical advice. Early intervention is key to managing potential complications that might arise from lung involvement.
Being informed not only improves patient care but also empowers those affected to seek timely medical advice when they notice changes in their health.
Associated Symptoms and Conditions
Malt lymphoma is often not an isolated entity; it comes with a variety of associated symptoms and conditions that can complicate the understanding of this disorder. When discussing malt lymphoma, recognizing these related symptoms is crucial for several reasons. First, they can serve as red flags indicating more complicated disease processes. Second, understanding these associations aids in developing an effective management strategy for patients. In this section, we will delve into the signs of immune system compromise and the relationship between malt lymphoma and other lymphoproliferative disorders.
Signs of Compromise in the Immune System
One of the primary concerns with malt lymphoma is its potential to compromise the immune system. Individuals with this condition may display certain signs that signal a weakened immune response.
- Frequent Infections: Patients might find themselves battling recurrent infections that wouldn't typically affect otherwise healthy individuals. Common colds or more severe infections could become a regular nuisance.
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of exhaustion is common. This fatigue often stems from the body working overtime to fight off abnormalities created by the cancerous cells.
- Fever: Unexplained fevers can emerge as the body reacts to lymphatic activity or systemic inflammation. This symptom often raises concern, as many patients may dismiss it as merely a flu.
- General Health Decline: There may be a noticeable decline in overall well-being. Weight loss, reduced appetite, and malaise are all signs that the body isn't functioning at its best.
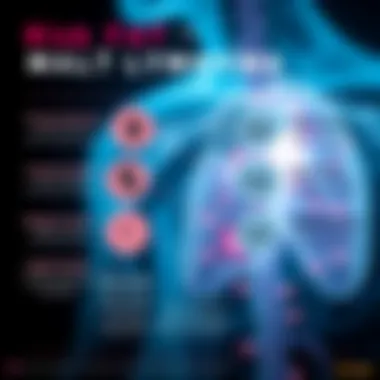
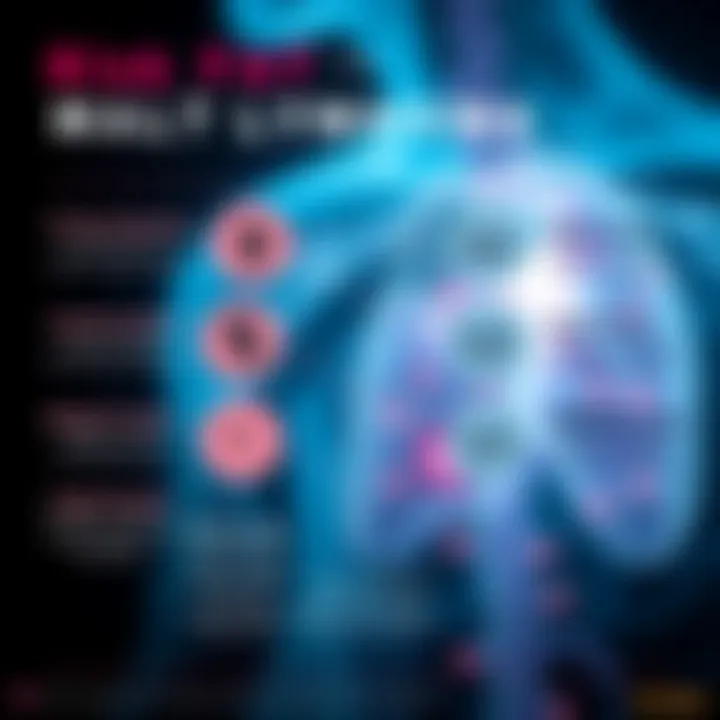
These symptoms not only underscore the physical toll of malt lymphoma but also highlight the need for a comprehensive evaluation to ensure the patient receives all necessary interventions.
"Addressing the immune system's challenges is paramount in managing malt lymphoma effectively."
Relation to Other Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Malt lymphoma doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It is part of a broader spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders, which can influence both diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the relationships among these conditions offers deeper insights into malt lymphoma itself.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Some patients with malt lymphoma may also exhibit characteristics that align with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It's not uncommon for the two to coexist, which complicates treatment.
- Follicular Lymphoma: Like malt lymphoma, follicular lymphoma is a non-Hodgkin variant that can affect the same immune pathways and may occur concurrently. This interplay can impact symptom management strategies.
- Marginal Zone Lymphoma: This disorder shares a close relation with malt lymphoma, as both originate from similar lymphatic tissues, primarily at mucosal sites. Recognizing this relationship is vital for effective diagnostic workflows.
Understanding the interplay between malt lymphoma and other lymphoproliferative disorders can significantly affect patient care. Considerations for treatment and diagnosis need to encompass a broad view of all potential related disorders.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnostic approaches to malt lymphoma are crucial for establishing an accurate diagnosis and initiating timely treatment. Considering the heterogeneity of symptoms associated with malt lymphoma, a structured diagnostic process is indispensable. This segment delves into the methods employed in diagnosing malt lymphoma, which form the backbone of effective patient management.
Initial Evaluation and Referral
In the initial evaluation of malt lymphoma, the focus is on patient history and physical examination. Common symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fatigue, or localized swelling can prompt further investigation. Practitioners often begin this process by assessing your symptoms against typical patterns observed in lymphoma cases.
Referral to a specialist, such as a hematologist or an oncologist, usually follows if these initial assessments raise suspicion of malt lymphoma. It’s essential for healthcare providers to remain vigilant, as early detection directly impacts prognosis.
In some cases, the provider may recommend preliminary tests including blood work which helps to evaluate the overall health and function of organs. This initial triage phase sets the stage for more advanced diagnostic techniques down the line.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
Once malt lymphoma is suspected, various diagnostic imaging techniques come into play. Imaging studies provide visual insight into the lymphatic system and any potential mass formations linked with the disease. The following methods are commonly employed:
- CT Scan: Primarily used to identify any abnormal masses in abdominal or chest regions.
- MRI: Offers a detailed view of structures, particularly helpful if lymphomas infiltrate soft tissues.
- PET Scan: This technique can highlight areas of high metabolic activity, which is indicative of cancer cells.
Each imaging modality has its own advantages and disadvantages. For instance, while a CT scan is excellent for visualizing larger masses, an MRI may be more sensitive to smaller lesions. In general, these imaging techniques guide the clinician in understanding the extent of the disease, which is crucial for developing an effective treatment strategy.
Biopsy and Histopathological Examination
Finally, a definitive diagnosis of malt lymphoma is achieved via a biopsy. This involves taking a small sample of tissue from the suspected site, which can be evaluated histopathologically. The importance of this step cannot be overstated, as it allows for:
- Classification of the Lymphoma: Determining the specific subtype, which can greatly influence treatment protocols.
- Identifying the Tumor Microenvironment: Understanding the associated immune responses can help predict patient outcomes.
The biopsy may be performed using various approaches, including endoscopic techniques for gastrointestinal symptoms or needle aspirations for more superficial nodes. Once the sample is obtained, pathologists analyze it under a microscope and may conduct immunohistochemical stains to further clarify the diagnosis. The precision gained from this step underlines its importance in guiding subsequent therapeutic decisions.
Symptom Management
Effectively managing symptoms associated with malt lymphoma is crucial for improving the overall quality of life for those affected. Given the variable nature of the disease, which can manifest differently from person to person, a tailored approach to symptom control is enevitable. Comprehensive symptom management not only enhances physical well-being but also supports psychological resilience in patients. As such, understanding the various strategies available—be it through pharmacological means or supportive therapies—plays an important role in patient care.
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions can provide significant relief from symptoms experienced by those with malt lymphoma. Medications are often prescribed based on the specific symptoms that manifest. A common approach includes:
- Chemotherapy: This is usually the first line of treatment for controlling tumor growth. Drugs like Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, and Prednisone may be used to alleviate symptoms arising from lymph node enlargements.
- Targeted therapies: These are designed to target specific pathways implicated in the growth of lymphoma cells. Agents like Rituximab may be utilized when appropriate, especially for patients exhibiting B-cell characteristics.
- Symptom-Specific Medications: For instance, patients who encounter pain may be prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or opioids, depending on the severity of the pain. Similarly, if the patient is battling nausea, antiemetics like Ondansetron can be effective.


A proper pharmacological regimen is also supplemented by regular monitoring to adjust medications as the condition evolves. Physicians typically assess the effectiveness and side effects of the prescribed treatments to ensure optimal management.
"Tailoring therapy to the individual is like fitting a suit; it needs to match perfectly to be effective.”
Supportive Therapies
Supportive therapies serve as a cornerstone for managing the symptoms of malt lymphoma, aiming to make patients as comfortable as possible. These therapies can enhance the effectiveness of pharmacological approaches and often include:
- Physical Therapy: Designed to improve mobility and reduce discomfort, physical therapy can help restore strength, especially for those who may be bedridden or experience fatigue.
- Nutritional Support: Maintaining a balanced diet can be vital, especially since some patients may face eating difficulties. Nutritionists can provide dietary plans that cater to the individual’s needs, ensuring they receive essential nutrients while alleviating discomfort.
- Psychosocial Support: Counseling services or support groups can play an essential role in helping individuals deal with the emotional ramifications of their diagnosis. Being able to share experiences and feelings can foster a sense of community and understanding.
- Complementary Therapies: Modalities such as acupuncture, meditation, or yoga are increasingly recognized for their potential benefits in managing stress and promoting relaxation.
By addressing the various dimensions of health—physical, emotional, and social—supportive therapies can substantially improve a patient’s overall experience in dealing with malt lymphoma. Every aspect holds its own significance, but together they form a network of care that supports patients on multiple fronts.
Prognostic Implications of Symptoms
Malt lymphoma, though often viewed through the lens of its clinical presentation, carries profound implications for prognosis dependent on the symptoms exhibited. Understanding the relationship between these symptoms and the disease's trajectory can offer invaluable insights for both patients and healthcare professionals. The manifestations of malt lymphoma are not mere anomalies; they serve as indicators that may influence treatment strategies and predictions about disease outcomes.
Impact on Disease Progression
When it comes to malt lymphoma, the particular symptoms a patient presents can offer a window into the disease's behavior. Symptoms such as persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or swollen lymph nodes might indicate a more active disease process. Early recognition of these signs is crucial. For instance, patients showing systemic symptoms are often facing a higher risk of aggressive disease progression.
- A study highlighted that patients who exhibited more severe symptoms at presentation often encountered quicker advancements in their conditions.
- Moreover, localized symptoms, while seemingly less concerning, can also hold significance. In some cases, they may signal a shift in disease status, warranting closer monitoring and possible intervention.
To illustrate, consider a patient presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms such as recurrent nausea and abdominal pain. These could indicate the lymphoma's involvement in gut-associated lymphoid tissue, hinting at a more complicated prognosis compared to those experiencing purely localized symptoms like ocular issues.
Correlation with Treatment Outcomes
Symptoms can shape not only the progression of malt lymphoma but also the effectiveness of its treatments. Research underscores that specific symptoms may correlate strongly with how patients respond to various therapeutic approaches. Patients exhibiting early signs of the disease are generally more responsive to standard treatment modalities compared to those with late-stage symptoms, which often entail more complex clinical management.
- For example, patients who present with mild symptoms may achieve better outcomes with first-line therapies, like antibiotics or monoclonal antibodies, as opposed to those who come in with extensive systemic involvement needing aggressive treatments like chemotherapy.
- Furthermore, symptomatic expression can influence decision-making regarding treatment intensity and options. Clinicians often weigh the symptomatic severity against treatment risks to tailor individualized plans for optimal outcomes.
This nuance emphasizes the necessity for continuous monitoring of symptoms throughout a patient's journey with malt lymphoma. Understanding how symptoms correlate to treatment responses fosters a more strategic approach to medical care.
"The symptoms of malt lymphoma are not just what the patient experiences; they are a map guiding clinicians toward tailored treatment pathways."
In summary, recognizing the prognostic implications of symptoms in malt lymphoma goes beyond the realm of patient experience; it becomes an integral part of clinical decision-making and long-term management strategies. This understanding aids in fostering informed patient choices and ultimately enhances care outcomes.
Ending
In wrapping up our examination of malt lymphoma symptoms, it becomes clear that understanding this condition is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals. This final section serves to underscore the multifaceted nature of malt lymphoma, offering a synthesis of key insights gathered throughout the article.
Summary of Key Insights
Malt lymphoma presents various symptoms that can often lead to confusion or misdiagnosis. Here are some pivotal points to take away:
- Diversity of Symptoms: The symptoms of malt lymphoma often vary widely among individuals. While some may experience mild discomfort, others may face more severe manifestations that affect their quality of life.
- Localized vs Global: Recognizing the difference between localized and systemic symptoms is crucial. Localized symptoms may be easier to identify, whereas systemic indications might point to more advanced disease.
- Chronic Nature of Symptoms: Many symptoms can be chronic, making the awareness of potential signs essential for timely diagnosis.
In addition, the article highlighted potential signs of immune system compromise and related health conditions. Understanding these aspects not only aids in the identification of malt lymphoma but also supports better patient management.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, research into malt lymphoma is essential for improving diagnosis and treatment options. Future investigations could focus on several areas:
- Genetic Factors: Delving deeper into the genetic predisposition of malt lymphoma may open doors to personalized treatment plans, enhancing outcomes for patients.
- Treatment Modalities: Exploring innovative treatment approaches, including immunotherapy or targeted therapies, could significantly alter the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with this condition.
- Highlighting Environmental Influences: Understanding the role of environmental factors in the pathogenesis of malt lymphoma can provide insights that promote preventative measures.
The ongoing advancement in research could very well redefine how we approach malt lymphoma, shifting the focus from mere symptom management to tangible curative efforts.
As healthcare professionals and patients alike stay informed about malt lymphoma, the hope is that a better understanding of its symptoms, implications, and treatment will emerge from persistent scholarly inquiry. The knowledge we build today paves the way for enhanced care and improved futures for those affected by this complex disease.







