Understanding Psoriasis Atopica: Challenges and Treatments

Intro
Psoriasis atopica represents a niche yet significant variant of psoriasis, distinguished by its inflammatory skin lesions and unique clinical challenges. Although this condition is often overshadowed by more widely understood skin disorders, it demands attention due to its complex etiology and pathophysiology. This article aims to traverse the multifaceted landscape of psoriasis atopica, providing vital insights for healthcare professionals, researchers, and students in the field. By delving deeply into the definition, symptoms, treatment modalities, and current research, we aim to furnish a thorough understanding that supports better management strategies and patient care.
Key Concepts and Terminology
Definition of Key Terms
- Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell production leading to thickened patches of skin, often covered with silvery scales.
- Atopica: Refers to the association with allergic conditions; in this context, it highlights the potential immunological and genetic factors at play in psoriasis atopica.
- Inflammatory skin lesions: Skin changes marked by redness, swelling, and possible scaling, indicative of underlying immune system activity.
Concepts Explored in the Article
This exploration prioritizes numerous key concepts:
- The etiology of psoriasis atopica, including genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
- The pathophysiology, detailing how this condition manifests through altered skin cell dynamics and inflammatory processes.
- A comprehensive overview of clinical manifestations, which aids in distinguishing psoriasis atopica from other dermatological conditions.
- An in-depth look at management strategies, including systemic therapies and emerging biologics, essential for optimizing patient outcomes.
Findings and Discussion
Main Findings
The research indicates that psoriasis atopica may share overlapping characteristics with atopic dermatitis and allergic responses. Understanding the classifications and diagnostic criteria plays a crucial role in differentiating it from similar skin conditions. Recent studies underline the importance of personalized treatment approaches. Strategies should consider not only the individual needs of patients but also the environmental and genetic factors contributing to their condition. Recent advances in systemic therapies, including biologics like Secukinumab, have shown promise in managing skin lesions effectively.
"Understanding the complexities of psoriasis atopica is imperative for developing effective therapeutic strategies that lead to enhanced patient care and outcomes."
Potential Areas for Future Research
Future research could focus on several pivotal areas:
- The role of genetics: Investigating specific genetic markers associated with psoriasis atopica.
- Longitudinal studies: To evaluate the efficacy of new treatments over time and their impact on quality of life.
- The influence of environmental factors: Understanding how lifestyle and environmental triggers may exacerbate or alleviate symptoms.
By addressing these areas, the dermatological community can further comprehend the intricacies surrounding psoriasis atopica and improve therapeutic protocols.
Prelude to Psoriasis Atopica
Psoriasis atopica, often overlooked in dermatological discussions, presents a unique blend of challenges. Understanding this condition is crucial as it affects a notable segment of the population. This article aims to delve into various aspects of psoriasis atopica, including its definition, historical context, and beyond. By illuminating these facets, we underscore the significance of comprehension surrounding this skin disorder.
Definition
Psoriasis atopica is characterized by inflammatory skin lesions. Unlike the more commonly known psoriasis types, this variant has its own distinctive features. Patients often experience patches that are itchy and may become red and scaly. These manifestations pose both discomfort and societal challenges. Clarifying the definition allows us to delineate psoriasis atopica from other skin conditions, leading to better diagnosis and management.
Historical Context
Historically, psoriasis has been documented for centuries. The evolution of its understanding reveals the complexity of psoriasis atopica. Initially, many terms were used interchangeably to describe skin lesions. Over time, advancements in medical science have led to a more nuanced classification. Research into psoriasis atopica has increased, unveiling its specific characteristics and responses to treatment. This historical backdrop is vital in tracing how perceptions and treatment options have evolved.
"As our understanding of psoriasis improves, it becomes essential to recognize the distinctions among its various forms, particularly psoriasis atopica."
The journey from vague descriptions to defined criteria illustrates the importance of ongoing research and awareness for effective patient care.
Epidemiology
The field of epidemiology is crucial for understanding psoriasis atopica, as it provides insights into how widespread this condition is, what groups of people are affected, and how it influences public health. Knowledge of epidemiological patterns helps in the formation of targeted healthcare policies and resource allocation. It also aids healthcare professionals in recognizing high-risk groups and tailoring interventions accordingly. By examining prevalence, incidence, and demographic factors, we can cultivate a comprehensive understanding of this dermatological condition.
Prevalence and Incidence Rates
Prevalence rates of psoriasis atopica can vary significantly depending on geographical regions and demographic factors. In general, it is observed that this form of psoriasis affects a relatively small percentage of the general population, often reported to be around 0.5% to 2%. However, these numbers may not fully capture the extent of the condition due to underdiagnosis and variances in healthcare access.
Incidence rates also provide valuable information. Incident cases often peak in adulthood, specifically between the ages of 20 and 50. Young adults appear particularly vulnerable, though onset can occur at any age. Recent studies suggest that both genetic predisposition and environmental factors contribute to the rising incidence rates in certain populations.
Demographics
The demographics of psoriasis atopica reveal disparities among different populations. Specifically, the condition seems to manifest with greater frequency in women compared to men. Moreover, ethnic backgrounds play a significant role. For instance, Caucasians show higher rates of the disorder compared to African American and Asian groups.
Age is another demographic factor, as younger individuals show earlier presentations of symptoms, while older adults may experience a different or less aggressive type of psoriasis atopica. Awareness of these demographic trends allows for more effective public health measures targeted at at-risk populations. Integrated analyses can also help to refine therapeutic approaches to better serve the unique needs of these groups.
Etiology of Psoriasis Atopica
Understanding the etiology of psoriasis atopica is crucial for several reasons. First, it allows healthcare professionals to identify and implement effective treatment strategies tailored to individual patients. By analyzing the root causes of this variant of psoriasis, practitioners can better educate patients about their condition and manage expectations regarding treatment outcomes. The complex interplay among genetic, environmental, and immunological factors can provide insights into disease progression and response to therapies, potentially leading to improved patient care.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predisposition is a significant component in the development of psoriasis atopica. Numerous studies indicate that a family history of psoriasis can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. Specific genes associated with immune function, such as HLA-Cw6, have been linked to psoriasis susceptibility. Furthermore, variations in the IL-23 receptor gene can influence the inflammatory response in affected individuals, suggesting that genetic factors dictate not only susceptibility but also the severity and progression of the disease. Understanding these genetic elements can aid in personalized treatment approaches, allowing for targeted therapies that align with an individual’s genetic make-up.
Environmental Triggers
In addition to genetic components, environmental factors can significantly impact the onset and exacerbation of psoriasis atopica. Common triggers include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can worsen inflammation and flare-ups.
- Infections: Certain infections, especially streptococcal throat infections, are linked to the onset of psoriasis.
- Skin Trauma: Injuries or skin irritations can instigate psoriatic lesions.
- Climate: Extremes in weather, either excessive humidity or dryness, can affect skin health, unaffecting the dermatological landscape.
Awareness of these triggers allows patients to adopt preventive measures, such as stress management techniques and maintaining a stable climate for their skin, contributing to better disease management.
Immune System Involvement
The immune system plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis atopica. It is characterized by an inappropriate immune response where T cells, a type of white blood cell, become activated and produce inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines contribute to the hyperproliferation of skin cells, leading to the characteristic lesions. A malfunction in the immune response can trigger skin inflammation and accelerate the turnover of skin cells, causing the rapid growth observed in psoriasis. Understanding immune system interactions helps researchers explore novel therapeutic strategies, particularly biologics that target specific pathways in the immune response.
"A clear understanding of the etiology is essential for developing effective management strategies for psoriasis atopica."
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of psoriasis atopica provides essential insights into the disease mechanisms, revealing the interplay between skin structure and immune response. Understanding these elements allows clinicians to develop targeted treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes. Moreover, it guides researchers in exploring innovative therapeutics that address the condition's underlying causes rather than merely its symptoms.
Skin Changes
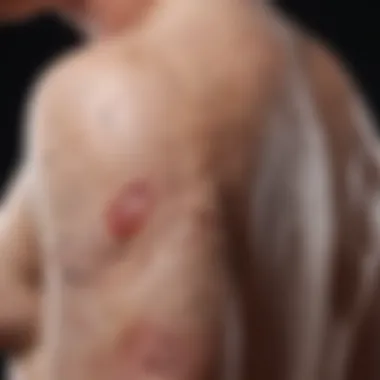
In psoriasis atopica, characteristic skin changes play a pivotal role in the clinical presentation. The epidermis undergoes hyperproliferation, resulting in thickened, scaly plaques. Typically, the normal cell turnover cycle takes about 28 days; however, in this form of psoriasis, it can occur within 3 to 5 days. This accelerated process leads to an accumulation of immature keratinocytes. Consequently, the outer layer of skin becomes red, inflamed, and covered with silvery scales, often causing discomfort or itching for the affected individuals.
"Increased skin cell production is a hallmark of psoriasis atopica, reflecting a crucial aspect of its pathophysiology."
The dermal layer also experiences changes, such as increased vascularization. This contributes to the redness and inflammation that are typical in affected areas. Dendritic cells, which are crucial for the immune response, infiltrate the epidermis and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukins, perpetuate the inflammatory cycle and promote further skin changes.
Heather-like Inflammation
Heather-like inflammation is a distinct feature of psoriasis atopica. This term describes the infiltration of immune cells, particularly T cells, into the skin, which resembles a dense, like-heather plant growth.
This inflammatory process typically manifests as erythema and scaling in various locations, depending on individual patterns of the disease. The immune system's overactivity in psoriasis atopica leads to this excessive inflammation, contributing to the painful skin lesions and associated symptoms, such as burning or stinging sensations.


The condition is not merely a skin ailment; it can affect the deeper tissue structures. Chronic inflammation may also predispose individuals to comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis and metabolic syndrome. Therefore, recognizing heather-like inflammation is crucial not only for diagnosis but also for formulating a comprehensive patient management plan that addresses both skin health and systemic implications.
Understanding the complex mechanism of pathophysiology in psoriasis atopica allows healthcare professionals to tailor interventions that optimize treatment efficacy and improve the quality of life for patients.
Clinical Manifestations
Understanding clinical manifestations is crucial in the context of psoriasis atopica. These manifestations not only aid in diagnosis but also inform treatment strategies. By being aware of the specific signs and symptoms of this condition, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients. This section dives into the common symptoms and distinct characteristics of lesions associated with psoriasis atopica.
Common Symptoms
Psoriasis atopica presents a range of common symptoms that can vary in severity. Patients often experience:
- Red patches of skin: These are inflamed and can be covered with silvery-white scales, indicative of rapid skin cell turnover.
- Itching and burning sensations: Many individuals report discomfort that tends to vary in intensity.
- Dry, cracked skin: This adds to the distress as it may cause bleeding or pain.
The recurrence of symptoms in outbreaks can lead patients to seek immediate care, highlighting the essential need for early intervention. Moreover, itching and discomfort can significantly impair quality of life, further emphasizing the importance of recognizing these symptoms promptly.
Lesion Characteristics
Lesions associated with psoriasis atopica have specific characteristics that set them apart from those seen in other dermatological conditions. The following points summarize some key features:
- Size and Shape: Lesions can be small or large and are often well-defined. The shape is typically round or oval.
- Surface Texture: The lesions may have a scaly surface, primarily due to the excessive buildup of skin cells.
- Location: Common areas for lesions include elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. However, psoriasis atopica can also present in atypical areas such as the genitals.
Important Note: Understanding the characteristics of these lesions is vital for differential diagnosis, especially to distinguish psoriasis atopica from other skin conditions.
Detailing the clinical manifestations helps in constructing a clearer picture of psoriasis atopica, which is essential for effective management and treatment tailored to individual patient needs.
Classification
The classification of psoriasis atopica holds considerable significance in understanding and managing this condition. It facilitates an organized approach to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the various types of psoriasis helps clinicians recognize distinct patterns that may dictate specific therapeutic strategies. Additionally, proper classification plays a crucial role in research, aiding in the development of more targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several recognized types of psoriasis, each with unique features. This section highlights the primary types:
- Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with thick, silvery scales. It often appears on elbows, knees, and the scalp.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Generally starts in childhood or young adulthood. It presents as small, drop-shaped lesions, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This manifests as bright red, shiny lesions found in skin folds, such as under the breasts or in the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules of noninfectious pus surrounded by red skin. This type can appear in localized patches or cover large areas.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe type that can affect the entire body, leading to widespread redness and shedding of skin. It can be very serious and requires immediate medical attention.
Each type serves as a distinct category, aiding in the comprehension of the disease's complexity and allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment appropriately. This knowledge is particularly crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms that may not fit common presentations.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is a vital process in clinical evaluation, particularly concerning psoriasis atopica. It involves distinguishing psoriasis from other dermatological conditions that may present with similar symptoms.
Conditions that need consideration include:
- Eczema: Often confused with psoriasis, eczema typically features intense itching and may not have the characteristic plaques of psoriasis.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This condition can appear oily and is often found on the scalp, similar to scalp psoriasis but lacks the typical plaques.
- Fungal Infections: Certain fungal infections can mimic psoriatic lesions, requiring careful examination.
- Lichen Planus: This condition presents with purplish, itchy spots that, while distinct, sometimes overlap with psoriasis features.
- Drug Reactions: Certain medications can lead to a rash that resembles psoriasis and must be ruled out.
The implications of differential diagnosis extend beyond mere identification; they can significantly influence treatment decisions. Misdiagnosis may lead to inappropriate management, thereby affecting the patient's quality of life.
Understanding the classifications and differentiating psoriasis atopica from other conditions is essential for effective patient management.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of psoriasis atopica is a crucial element in the management of the condition. Accurate diagnosis allows for the implementation of effective treatment strategies tailored to individual patient needs. In many cases, psoriasis atopica may be confused with other dermatological conditions. Therefore, a careful approach in diagnosing it can rid patients of unnecessary treatments that will not address their unique symptoms. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can lead to better patient outcomes.
Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination is the cornerstone of diagnosing psoriasis atopica. The dermatologist or healthcare provider inspects the skin for specific lesions and their distribution. Palpation may be used to assess the thickness and texture of the lesions, which can be characteristic of this condition.
During this examination, the healthcare professional will look for:
- Erythematous plaques
- Silvery scales that cover the lesions
- Surrounding skin changes
- Areas of linear or fresh lesions
Additionally, the patient's medical history and family history of psoriasis or related conditions are reviewed. This history can provide insight into potential genetic factors and environmental triggers.
Diagnostic Imaging
While diagnostic imaging plays a minor role in the diagnosis of psoriasis atopica, it can be useful in cases where joint involvement is suspected. Tools such as ultrasound or MRI may be employed to visualize underlying joint inflammation. This is particularly important as psoriatic arthritis can coexist with psoriasis atopica, complicating the clinical picture.
"Imaging techniques can help in understanding the extent of disease, especially when systemic therapy is considered."
Radiologic imaging assists in evaluating joint inflammation that might not be clinically evident. However, clinical examination remains the primary means for skin diagnosis.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests can further support the diagnosis but should not be the sole basis for it. Routine blood tests may be conducted to:
- Rule out other conditions, such as allergies or infections
- Check for systemic involvement that can arise from other comorbidities
The tests may include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP) levels
These tests help assess inflammation in the body and provide insight into overall health status. However, no specific laboratory test can definitively diagnose psoriasis atopica on its own.
In summary, the diagnosis of psoriasis atopica requires a combination of clinical examination, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory test interpretation. A comprehensive approach can lead to accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Treatment Options
Understanding the various treatment options for psoriasis atopica is crucial in managing the condition effectively. Treatment strategies often depend on the severity of the disease, the individual's health status, and response to prior therapies. Proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for patients, reduce flare-ups, and enhance skin health. Moreover, awareness of available treatments helps empower patients in discussions with healthcare providers. Here we explore topical treatments, systemic therapies, and biologics in depth.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are usually the first line of defense against psoriasis atopica. These treatments are applied directly to the skin and are designed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Common topical treatments include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids. Each has its specific benefits and limitations.
- Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can quickly reduce redness and irritation. They work by suppressing the immune response and decreasing inflammation.
- Vitamin D analogs can slow the growth of skin cells. They are commonly used alongside corticosteroids to potentiate their effects and reduce reliance on more potent steroids.
- Retinoids, which are derived from vitamin A, are effective in normalizing skin cell growth. They can also have anti-inflammatory benefits.
Patients should consider potential side effects when using topical therapies, such as skin irritation or thinning, and the need for regular application. It is often necessary to adjust the strength or type of medication based on individual response.
Systemic Therapies
Systemic therapies are more intensive treatments that affect the entire body. They are typically reserved for moderate to severe psoriasis rooftops that do not respond adequately to topical treatments. These therapies include oral medications and injectable drugs that alter the immune system or inflammatory processes in the body.
- Methotrexate is a common systemic therapy that reduces rapid skin cell growth and modulates the immune response. It must be monitored for potential liver toxicity and other side effects.
- Cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant that can yield rapid results but carries a risk of serious side effects, particularly kidney damage with long-term use.
- Oral retinoids, such as acitretin, can also be effective. They help normalize skin cell growth but may have significant side effects, including teratogenicity in women of childbearing age.


Patients must engage in thorough discussions with their healthcare providers when considering systemic therapies, as these treatments often require regular blood monitoring and have various contraindications.
Biologics
Biologics represent a newer class of therapies specifically designed to target particular components of the immune system. They are administered either through injection or infusion and are considered for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis atopica who have not responded to other treatments.
Some key biologics include:
- Adalimumab and Etanercept, which target tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), a key player in the inflammatory process.
- Ustekinumab targets interleukin-12 and interleukin-23, helping to dampen the inflammatory response.
- Secukinumab and Ixekizumab target interleukin-17, a cytokine released during inflammation.
Biologics have been shown to be effective in controlling symptoms and improving patients’ quality of life. However, they also come with their own set of risks, including increased susceptibility to infections due to immune modulation.
"The choice of therapy for psoriasis atopica should always be tailored to the individual patient's needs and medical history. Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential to find the most effective treatment strategy."
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a vital role in the management of psoriasis atopica. These changes can enhance the overall well-being of patients and may significantly reduce flare-ups or exacerbate symptoms. Addressing various aspects of daily life such as diet, stress, and skincare routines is crucial in creating a holistic approach to treatment. Adjustments in lifestyle often become a critical part of managing this chronic condition, facilitating patients in navigating their daily challenges more effectively.
Diet and Nutrition
The relationship between diet and skin health is widely recognized. Several studies suggest that certain dietary choices can improve the condition of the skin in individuals with psoriasis atopica. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can be beneficial. This might include omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds. These foods can help reduce inflammation, potentially alleviating some symptoms of psoriasis.
Reducing the intake of processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats can also have positive effects. Some individuals may benefit from avoiding lactose and gluten, as these can be triggers for some. It is essential that patients explore their dietary sensitivities. Keeping a food diary could help determine what works or doesn’t for each individual.
Key dietary tips include:
- Focus on whole foods: Vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough water is important for overall health and skin hydration.
- Limit alcohol: Alcohol may worsen psoriasis symptoms in some patients.
Stress Management
Stress is widely acknowledged as a significant trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Managing stress effectively is essential for patients dealing with this condition. High levels of stress can provoke immune responses that aggravate skin lesions and lead to worsening symptoms.
Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga may aid patients in reducing anxiety and improving mental health. Regular physical activity is also vital; it promotes the release of endorphins, leading to improved mood and relaxation.
Furthermore, establishing and maintaining a healthy work-life balance can contribute to better stress management. Support from friends, family, and counseling may also provide additional help.
Common stress management techniques:
- Mindfulness practices: This includes meditation or breathing exercises.
- Engaging in physical activities: Regular exercise can significantly reduce stress levels.
- Time management: Prioritizing tasks can help alleviate feelings of being overwhelmed.
Skincare Routines
A proper skincare regimen is fundamental for those with psoriasis atopica. The skin barrier often becomes compromised in individuals with this condition, leading to dryness and irritation. Therefore, patients need to invest in a consistent skincare routine that prioritizes hydration and protection.
Using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers can prevent further irritation. Moisturization is paramount; applying emollients after bathing or showering can lock in moisture. It is beneficial to use thick creams or ointments rather than lotions, as they provide better hydration.
Effective skincare tips include:
- Moisturize frequently: Especially right after bathing to maintain skin hydration.
- Use lukewarm water: Hot water can strip the skin of natural oils.
- Protect skin from harsh weather: Cover skin in cold weather and use sun protection in warmer months.
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine plays a crucial role in reducing symptoms and improving the quality of life for many psoriasis atopica patients.
Through these lifestyle modifications, individuals suffering from psoriasis atopica can take proactive steps toward managing their condition. Integrating these changes into daily routines can result in improved health outcomes and a heightened sense of control over one's well-being.
Patient Management
Effective patient management is critical in addressing psoriasis atopica, an inflammatory skin condition that presents numerous challenges. Due to its complex nature, comprehensive management strategies are essential for improving patient outcomes. A well-structured patient management plan can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals suffering from this condition.
Long-term Care Strategies
Long-term care strategies for psoriasis atopica involve continuous monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans. These strategies are vital in managing the chronic nature of the disease, ensuring patients remain engaged and informed about their condition. Regular follow-ups with dermatologists often include:
- Assessment of skin lesions and overall skin health.
- Evaluation of treatment effectiveness and potential side effects.
- Adjustments in therapy based on disease progression.
Proactive management can lead to improved adherence to treatment regimens. Patients educational resources can also empower individuals to take control over their condition. Knowledge regarding triggers, lifestyle changes, and self-care practices plays a crucial role in reducing flare-ups.
"Continuous education and communication between the physician and patient are fundamental for effective long-term management in psoriasis atopic."
Multidisciplinary Approach
A multidisciplinary approach in managing psoriasis atopica involves collaboration among various healthcare professionals. This can include dermatologists, rheumatologists, psychologists, and nutritionists. Each professional contributes a unique perspective to treatment:
- Dermatologists focus on immediate skin care and treatment plans.
- Rheumatologists may be involved if there are joint symptoms associated with the skin condition.
- Psychologists can help address mental health issues, which often accompany chronic conditions, enhancing the overall care strategy.
- Nutritionists can provide dietary recommendations that may positively influence skin health.
By coordinating between these specialties, the management of psoriasis atopica can become more holistic and tailored to individual patient needs. This integration of care not only addresses the physical symptoms but also considers emotional and psychological well-being, promoting comprehensive wellness.
In summary, patient management for psoriasis atopica is multifaceted. It combines long-term care strategies with a multidisciplinary approach, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and an improved patient experience.
Emerging Research and Developments
Emerging research in psoriasis atopica represents a critical avenue for advancing understanding and treatment of this condition. As new studies and developments unfold, they offer insights into the underlying mechanisms, potential therapies, and the overall management of psoriasis atopica. The importance of this research cannot be overstated, as it not only challenges traditional perceptions but also fosters innovative approaches to patient care.
Recent Studies
Recent research has shed light on various aspects of psoriasis atopica. Clinical trials have increasingly focused on novel therapeutic targets and methodologies. For instance, studies have identified specific biomarkers that may predict treatment response among patients. These biomarkers can provide valuable information to clinicians, informing more tailored treatment plans.
Additionally, significant efforts are being made to explore the role of the microbiome in skin health. Some studies suggest that alterations in skin microbiota may contribute to inflammatory processes, linking psoriasis atopica to broader systemic conditions. This line of research emphasizes the interconnectedness of various bodily systems and how they affect skin conditions.
In terms of pharmacological advancements, recent studies have evaluated new biologic therapies, which hold promise for individuals unresponsive to conventional treatments. Trials assessing dupilumab have shown positive outcomes in reducing the severity of lesions and improving patient quality of life.
"New therapies and research findings are crucial for evolving treatment paradigms and improving care strategies for psoriasis atopica."
Future Directions
The future of psoriasis atopica research appears promising, with a focus on several key areas. Firstly, continued exploration of genetic predispositions is likely to lead to a better understanding of who is at risk and how to intervene early. Understanding genetic markers can pave the way for preventive strategies.
Secondly, innovation in treatment development stands out as a major focus. Advances in targeted therapies are likely to evolve. More refined biologics that specifically address the unique pathways involved in psoriasis atopica will emerge. Future research may also delve into combination therapies, enhancing efficacy through synergy between various classes of medications.
Moreover, holistic approaches that consider lifestyle factors should gain attention. Integrating psychosocial aspects into treatment plans could foster a more comprehensive care model, addressing both the physical and emotional impacts of psoriasis atopica.
Lastly, advancements in digital health and telemedicine present new opportunities for patient monitoring and education. Remote tools can enhance access to specialists and provide continuous support to patients, especially in managing their condition over the long term.
In summary, the emerging research landscape for psoriasis atopica reflects an ongoing evolution in understanding and managing this complex condition. As new insights unfold, they will undoubtedly shape the future framework for patient care and therapeutic approaches.


Psychosocial Impact
The psychosocial aspects of psoriasis atopica hold significant relevance in understanding the comprehensive implications of this condition. Individuals with psoriasis atopica often face not just physical discomfort but also emotional and psychological strains due to their skin disease. These strains can lead to a diminished quality of life, whereby individuals may experience feelings of anxiety, depression, and isolation. The impact on mental health carries substantial weight and must be addressed comprehensively to improve overall patient well-being.
Mental Health Considerations
Mental health considerations are crucial for patients suffering from psoriasis atopica. Research indicates a common association between skin diseases and psychiatric disorders. Patients may feel embarrassed about their appearance, leading to social withdrawal and even avoidance of certain activities. Psychological distress is prevalent, with studies showing that individuals with psoriasis are at an increased risk for depression and anxiety.
Support systems play a vital role. Open discussions with healthcare providers can lead to better therapeutic outcomes. Mental health evaluations and counseling should be integral parts of the management plan for psoriasis atopica. This holistic approach can help in addressing not only the skin's symptoms but also the mental toll of living with the condition.
"Addressing the mental health impacts of skin conditions is as important as treating the skin itself."
Social Acceptance and Stigma
Social acceptance and stigma surrounding skin diseases are important facets to consider in the context of psoriasis atopica. Many patients report feeling judged based on their appearance, which can exacerbate feelings of shame or inferiority. Society's views on skin diseases can result in discrimination, affecting integration into social circles or even employment opportunities.
The stigma associated with visible conditions like psoriasis can inhibit individuals from seeking help or participating in activities they used to enjoy. Building awareness about psoriasis and its impact can play a critical role in reducing stigma. Education and advocacy efforts aimed at promoting understanding can transform perceptions.
Combating this stigma requires a concerted effort from not only healthcare professionals but also the community at large. Initiatives like support groups and social media forums, such as on reddit.com, can foster environments where patients feel accepted and understood.
In summary, recognizing and addressing the psychosocial impact of psoriasis atopica is essential. The mental health considerations and societal challenges that patients face must be thoroughly integrated into care strategies, ensuring that treatment for psoriasis atopica is truly comprehensive.
Case Studies
Case studies serve as an essential component in understanding psoriasis atopica. They provide real-world examples that can illustrate the complexities of the condition, making them invaluable for both education and clinical practice. By studying these cases, healthcare professionals gain insight into diverse patient experiences and outcomes, highlighting the variable nature of the disease and its response to treatments.
Through case studies, we can identify patterns that might not be evident in clinical trials. They offer perspectives on comorbidities, socio-economic factors, and individual treatment responses that statistical data could overlook. Furthermore, these narratives can catalyze discussions on best practices and innovative approaches in managing psoriasis atopica.
Notable Cases
One significant case involved a 35-year-old female diagnosed with psoriasis atopica who presented with widespread lesions resistant to conventional treatments. Initial management focused on topical corticosteroids and moisturizers, commonly used in dermatology. While these produced limited results, subsequent introduction of systemic therapy showed marked improvement.
In another instance, a young male patient experienced severe psychological distress due to visible skin lesions. His treatment was combined with therapy aimed at addressing mental health concerns such as social anxiety. This highlights that treatment must consider not just physical but also psychosocial dimensions, showcasing the complexity inherent in psoriasis atopica management.
Clinical Response to Treatments
Clinical response to treatments varies significantly among patients with psoriasis atopica. Factors influencing these results include genetic predisposition, lesion characteristics, and the presence of other health issues. A growing body of evidence suggests that biologics like Adalimumab and Etanercept can lead to considerable improvements in skin condition, particularly in severe cases.
Key Takeaways
- Personalization of Treatment: Tailoring treatments based on individual responses is crucial.
- Multifactorial Treatment Plans: Incorporating psychological support with dermatological care can enhance overall outcomes.
- Awareness of Comorbidities: Recognizing and managing co-existing health conditions can improve treatment success.
Case studies play a vital role in enhancing our understanding of psoriasis atopica and refining management strategies. They offer clinicians deeper insights into patient experiences and treatment outcomes, guiding future research and practice.
To access more real-life discussions on psoriasis treatment and support, visit Reddit or explore informational resources on Wikipedia.
Understanding case studies not only enriches clinical knowledge but also emphasizes the need for ongoing research. Each case provides an opportunity to learn, adapt, and innovate in the treatment of psoriasis atopica.
Patient Education and Resources
Educating patients about psoriasis atopica is crucial for several reasons. Patients armed with knowledge can make informed decisions regarding their health and treatment options. Education helps them understand the condition better and equips them to manage it effectively. Moreover, patient education encourages active participation in treatment plans, which can lead to better adherence and outcomes.
An essential component of patient education is the availability of resources that provide reliable, accurate, and comprehensive information about psoriasis atopica. These resources should address the etiology, symptoms, available treatments, and how to effectively communicate with healthcare providers. This approach has the potential to significantly improve health literacy, empowering patients to advocate for themselves.
Support Groups
Support groups play a vital role in the educational landscape for individuals with psoriasis atopica. Joining a support network enables patients to connect with others facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of community. They provide a safe environment where individuals can share their experiences, coping strategies, and emotional responses to the condition.
Participating in such groups has been shown to have several benefits:
- Emotional support: Members can discuss feelings of isolation or stigma and receive encouragement from others who understand.
- Practical tips: Patients often share insights on managing symptoms, treatments they have tested, and resources that have worked for them.
- Access to experts: Many support groups facilitate meetings with healthcare professionals, allowing members to ask questions and gain further knowledge.
Online forums, such as those found on Reddit or Facebook, can also enhance accessibility by providing a platform for discussions at any time.
Informational Materials
The creation and distribution of informational materials are essential to patient education on psoriasis atopica. These materials should be clear, concise, and easily digestible. They can include brochures, pamphlets, and digital content.
Key elements to consider in these materials are:
- Visual aids: Diagrams and images can help illustrate the condition and its effects on the skin, making it easier for patients to understand.
- Multilingual resources: Providing materials in multiple languages ensures that non-native speakers also have access to critical information.
- Current treatment options: Updated information on the latest therapies, including biologics and systemic treatments, can guide patients in discussions with their healthcare providers.
Informational materials can be tailored to various audiences, from seasoned professionals to newly diagnosed patients. Distributing these materials through clinics, hospitals, and online channels ensures that they reach those who need them most.
End
In a comprehensive review of psoriasis atopica, the conclusion phase provides an essential summation of key insights. This section serves to reinforce the knowledge accumulated throughout the article, emphasizing the importance of recognizing the nuances of this health condition. Psoriasis atopica is not merely a variant of psoriasis; it presents its own set of challenges and implications for patient care.
Understanding this condition enables healthcare professionals to better address the specific needs of affected individuals. By summarizing key points such as the etiology, clinical manifestations, and emerging treatment options, the conclusion highlights how a thorough understanding can lead to improved patient outcomes. The benefits of effective management strategies are undeniable, especially when tailored to the patient's unique characteristics.
Importantly, ongoing research plays a vital role. The evolving landscape of treatment is promising, and future advancements may enhance therapeutic options. Recognizing the psychosocial impact is equally crucial, as mental well-being significantly affects adherence to treatment and overall quality of life for patients.
This article underscores the need for heightened awareness amongst both healthcare providers and patients. In the face of a condition often misunderstood or overlooked, informed discussions can lead to better diagnostic and therapeutic pathways.
Summary of Key Points
- Definition and Context: Psoriasis atopica is a unique variant of psoriasis, demanding a distinct approach in terms of treatment and management.
- Epidemiology: The prevalence and demographic factors influence how it manifests in different populations.
- Etiology and Pathophysiology: Key factors that contribute to the onset include genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, and immune system involvement.
- Clinical Management: Effective treatment options encompass topical treatments, systemic therapies, and biologics.
- Patient Education: Understanding the psychosocial aspects is essential to foster acceptance and adherence to treatment plans.
Future Considerations
As we look ahead, several aspects warrant attention. The future of psoriasis atopica management relies on the integration of personalized medicine approaches. Understanding that no two patients are alike forms the foundation for tailored treatment regimens.
- Emerging Therapies: Ongoing research into innovative treatments holds promise for more effective management.
- Longitudinal Studies: Future studies focusing on long-term outcomes associated with different therapies could provide invaluable insights.
- Impact of Lifestyle: Recognizing how lifestyle modifications can potentially alter the disease course should also be a priority.
- Support Systems: Continued emphasis on patient education and support mechanisms will empower those affected to manage their condition more effectively.
Importance of References
In our article, references serve several key functions:
- Source Validation: They support the data and information presented, helping to ensure that conclusions are based on sound research.
- Further Reading: For an audience seeking a deeper understanding, references direct readers to additional materials, enriching their knowledge.
- Scientific Rigor: Including up-to-date references from credible sources enhances the scientific rigor, which is essential in the medical field.
- Historical Context: Understanding psoriasis atopica requires some historical background. References can include seminal works that underline the evolution of thought surrounding this condition.
Some notable types of references include:
- Peer-reviewed articles from journals such as The Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
- Textbooks focusing on dermatology or immunology, which provide foundational knowledge.
- Guidelines from health organizations like the American Academy of Dermatology, which outline current best practices for diagnosis and treatment.
Considerations for References
When compiling references, it is important to consider:
- The relevance of the sources to the topic at hand.
- Publication date, ensuring that the information is current and reflects the latest research developments.
- The diversity of sources, utilizing both reviews and original studies to present a well-rounded view.
"An extensive understanding of any medical condition requires not only clinical data but also a background in historical context and ongoing research."







